In the realm of web development, the `hidden=until-found` attribute is garnering attention for its innovative approach to displaying hidden content. This HTML attribute enables developers to make elements invisible to users while still ensuring they are accessible through in-page search functionalities. By employing `hidden=until-found`, web designers can enhance web accessibility and improve user experience, creating content that can be found effortlessly even when it’s not visible on the page. As the web evolves, understanding how this feature interacts with existing standards like cross-browser support and content visibility becomes crucial. With better insights into `hidden=until-found`, developers can craft more intuitive and seamless browsing experiences for all users, regardless of the browser they use.
Exploring the notion of concealing elements on a webpage while maintaining their searchability brings us to the concept of `hidden=until-found`. This attribute not only allows developers to manage hidden content through HTML attributes but also significantly enhances web accessibility. As we work toward a more inclusive web environment, implementing techniques that support in-page search across different browsers is essential. By leveraging attributes that ensure content visibility and usability, web creators can offer a rich user experience. Understanding how these foundational elements of web design, such as the `hidden=until-found` attribute, operate will empower developers to produce more robust and user-friendly digital spaces.
Introduction to hidden=until-found
The advent of new HTML features continues to enhance user experience and accessibility on the web. One such feature is hidden=until-found, which has started gaining traction among developers. If you’re a WordPress enthusiast seeking robust yet economical hosting solutions, you might want to try Cloudways’ free trial. More importantly, understanding features like hidden=until-found can significantly improve how your content is presented, as it allows otherwise inaccessible content to be discoverable through in-page search functions.
Initially, when I encountered hidden=until-found in the Firefox 139 release notes, I felt a bit behind the curve—this was not new at all. Chrome had already integrated this functionality in 2022, while Safari seemed to be catching up. This feature essentially bridges a gap in content visibility without sacrificing usability, opening up discussions within the developer community about its implications and applications.
Functionality and Benefits
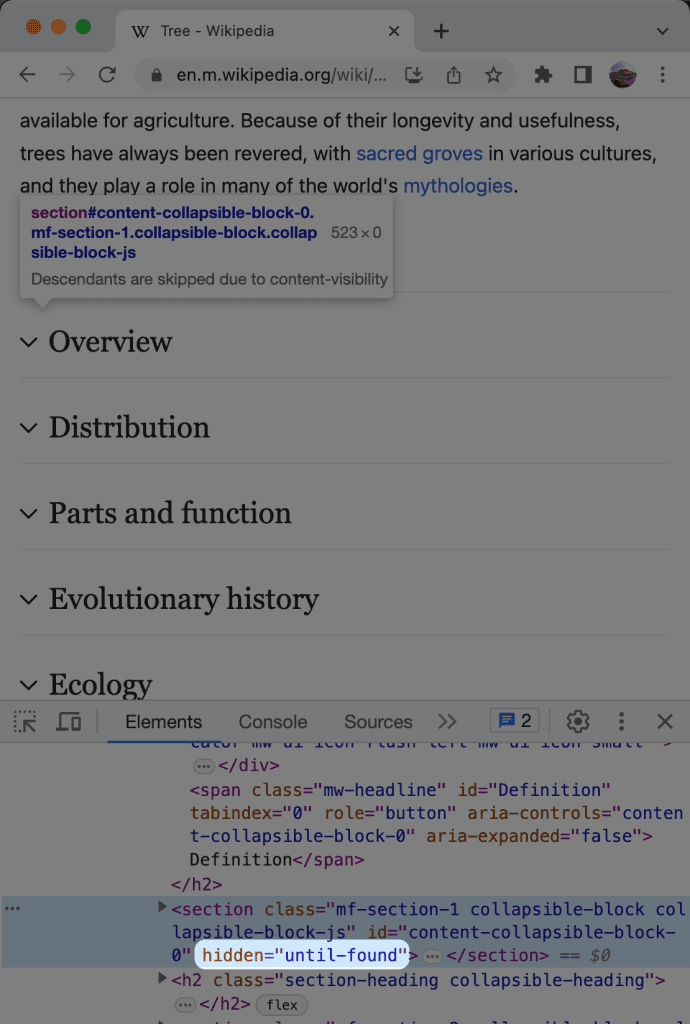
Hidden=until-found fundamentally provides a mechanism for developers to hide content that should remain searchable without necessarily displaying it upfront. For instance, embedding this attribute into an HTML element enables the content to become accessible when users try to search within the page. Utilizing the example provided by the code snippet, developers can ensure users still find relevant information, even if it isn’t immediately visible.
It’s comparable to having content-visibility: hidden but with critical modifications that prevent the content from being entirely barred from search functions. This subtle distinction is crucial for creating more dynamic and user-centered web experiences. The practical application of this feature often surfaces in environments where content is intentionally collapsed or revealed, such as accordions or FAQs.
Browser Support Landscape
Currently, Chrome and Firefox have embraced hidden=until-found, but Safari has lagged for some time. Nevertheless, its inclusion in the Interop 2025 roadmap suggests developments are on the horizon. Across the board, the promise of making hidden content searchable significantly enhances interactivity. For users navigating content-heavy sites, having hidden elements reveals new pathways for finding information efficiently.
In implementing solutions for better accessibility and user experience, developers often ponder whether hidden=until-found is the ultimate answer. The considerations for cross-browser compatibility remain at the forefront, as any deployment might necessitate custom fallbacks for unsupported browsers. The importance of ensuring a seamless user experience cannot be overstated, and developers like Nathan Knowler have paved the way by showcasing potential solutions—even as browser support continues to evolve.
Styling with hidden=until-found
While styling the hidden content itself may not seem imperative since users cannot visually interact with it, the in-page search feature brings a new dimension worth exploring. With search results highlighting matching queries, it creates motivation for developers to consider how these elements appear visually in those moments.
Looking ahead, speculations surrounding the introduction of a ::search-text pseudo-class could further amplify this feature. This would enable targeted styling for search results, allowing developers to choose colors or styles that correspond to user interactions. Such advancements could rethink not just how hidden content is accessed but also how it can be visually communicated through user interfaces.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the promise of hidden=until-found, some lingering questions remain regarding its long-term implementation. Developers may find themselves asking: what more could be done once a search query reveals content? Currently, matching results remain visible, becoming a source of potential confusion once a search is canceled. Understanding user context and pain points is essential for providing seamless functionality that aligns with their needs.
Looking toward the future, developers should continue engaging in dialogues about best practices for implementing such features. Innovating solutions while maintaining accessibility must remain paramount. The community will surely benefit from continuous contributions producing additional educational resources and collaborative efforts to steer functional advancements forward.
Conclusion and Resources
In conclusion, the introduction of hidden=until-found has sparked an important conversation about the evolution of content accessibility on the web. Users demand more from their digital experiences than just the basic find-in-page functionality—they expect enhanced interaction without compromise. As this feature becomes more mainstream and browser support solidifies, the landscape of web development will inevitably transform.
For further exploration, resources such as articles on polyfilling hidden until-found or announcements regarding Interop 2025 provide valuable insights. Engaging with them might yield a stronger foundational understanding that benefits projects for developers and non-developers alike.
Conclusion: The Significance of hidden=until-found
In wrapping up, the introduction of the hidden=until-found attribute significantly enhances the ways we can manage hidden content in web development. Not only does this HTML attribute allow for the seamless integration of content visibility and in-page search capabilities, but it also serves as a vital tool in improving accessibility across different browsers. Whether you’re developing a site that heavily relies on hidden content or simply want a more user-friendly interface, understanding and implementing this attribute can offer unique advantages.
To summarize its importance, consider the following points:
– **Findable Hidden Content**: Content wrapped in hidden=until-found remains hidden yet accessible during searches, enhancing user experience.
– **Broader Browser Compatibility**: As we transition towards Interop 2025, having support from Chrome, Firefox, and the upcoming Safari features ensures a more uniform experience for users.
– **Potential for Improved Styling**: With hints towards future updates in the CSS Pseudo-Elements Module, developers might gain more control over how search results are visually presented, further enhancing user interaction.
Final Thoughts on Accessibility and Development
The journey of web accessibility continues to evolve, and with features like hidden=until-found, developers have more options at their disposal to cater to diverse user needs. This evolution not only aligns with a more inclusive web design philosophy but also encourages developers to rethink how they implement hidden elements in their applications. As browser support expands, there’s a collective responsibility to leverage these advancements to create experiences that are both engaging and accessible.
Key takeaways for future considerations include:
– **Innovative Use Cases**: Explore and document new applications for hidden=until-found beyond conventional scenarios, enriching user experiences.
– **Accessibility Practices**: Make sure to integrate this attribute with other accessibility best practices to ensure that all users can navigate content effectively.
– **Continuous Learning and Adjustment**: The web development landscape is ever-changing; staying updated with the latest standards and browser features is vital to maintaining high-quality, accessible web applications.