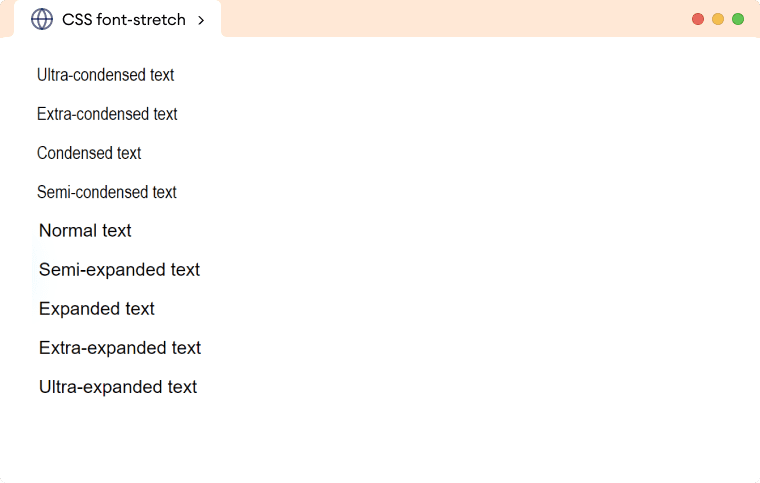
The CSS stretch keyword is an exciting addition to modern web design, providing developers with a powerful tool to optimize their layouts. Introduced in June 2025, this new CSS value works seamlessly with width and height properties to offer greater control over responsive design. Unlike traditional percentages, the stretch value takes padding into account, ensuring that elements fit perfectly within their containing blocks without overflow issues. This aligns with CSS layout best practices, enhancing the box model CSS and facilitating the creation of clean and adaptable styles. As web aesthetics continue to evolve, the stretch CSS value emerges as a game-changing asset for anyone looking to master CSS properties for responsive design.
In the realm of cascading style sheets, the term ‘stretch’ refers to a novel value that streamlines the process of setting element dimensions. This innovative addition allows developers to implement sizing that harmonizes perfectly with other properties like min-width and max-height. With a focus on achieving optimal layout consistency, this keyword simplifies controlling the spaces around elements, aligning well with contemporary CSS layout strategies. Additionally, the use of stretch can significantly improve the interaction between padding and element width, making it an essential feature for today’s modern web designs. By embracing this new nomenclature, designers can ensure their projects remain both functional and visually appealing.

The Inception of the Stretch Keyword
The stretch keyword made its debut in CSS as a welcomed addition, designed to improve how developers handle element dimensions. It surfaced in the Chromium browser family in June 2025, unifying two previously non-standard values: -webkit-fill-available from Safari and -moz-available from Firefox. This change addressed a significant gap that had persisted in CSS layout handling and offered a fresh perspective for managing widths and heights.
In the fast-paced world of web development, consistency across browsers is critical. Before stretch, developers often faced challenges catering to different browser behaviors, leading to potential oversights. The introduction of the @supports at-rule provided a mechanism for feature detection, yet many still overlooked the potential of stretch due to lack of awareness. Insightful contributors like Miriam Suzanne on Bluesky played a pivotal role in spreading knowledge about this innovative property.
Understanding the Functionality of Stretch
At its core, the stretch keyword operates similarly to a width or height of 100%. However, unlike a static 100%, it dynamically accounts for any padding applied to the element. In essence, this feature resolves common layout issues where developers previously struggled with overflow caused by padding values.
To illustrate this, consider a typical CSS example with a
Animating Elements with Stretch
One of the intriguing aspects of using stretch is its compatibility with CSS animations, a feature that traditional box-sizing methods lack. With stretch, developers have the opportunity to create more dynamic user interactions. For instance, by declaring an animation that transitions between width values, the stretch definition offers a fluid, responsive experience when hovering over elements.
In practice, implementing this feature involves setting up global declarations that enable the interpolation of size. A simple hover effect can transform a static element into an engaging visual experience. This not only enhances user interaction but also empowers developers with more design possibilities.
Browser Compatibility and Future Considerations
As of now, the stretch keyword is primarily supported in Chromium browsers, including Opera, Chrome, and Edge, illustrating the importance of keeping up-to-date with browser capabilities. For developers, this limited support underlines the necessity of considering fallbacks for unsupported browsers, allowing proper visual appearances regardless of user’s browser choice.
Implementing support through the @supports feature can help create a CSS that caters to various environments. By defining custom properties based on browser capabilities, developers can ensure that the layout functions seamlessly across platforms. As the CSS landscape evolves, we should anticipate broader support for the stretch keyword, leading to simpler and cleaner code.
Conclusion: Embracing New CSS Features
In conclusion, while the introduction of the stretch keyword may not revolutionize CSS as we know it, it undoubtedly enriches the toolkit available to developers. By simplifying layouts and enhancing responsiveness, it empowers web creators to write cleaner, more maintainable code. The evolution of web standards pushes everyone in the industry to adapt and incorporate new features.
Using stretch alongside existing methodologies ensures that developers are not only leveraging the best practices but are also future-proofing their designs. As we embrace these advances, it’s essential to relish the improvements they bring, making both our lives and our code a bit more enjoyable.
Embracing the Stretch Keyword
In conclusion, the stretch keyword in CSS represents a significant enhancement for web developers, particularly regarding how we handle dimensions within our layouts. While it may not seem revolutionary at first glance, its ability to harmonize the width and height properties with margin calculations can eliminate common pitfalls associated with overflow, thus leading to cleaner and more efficient code. This is particularly beneficial as more browsers adopt stretch, allowing web developers to use it without as many fallback methods, promoting a smoother coding experience.
Moreover, the transition capabilities provided by stretch open up new avenues for animations, creating dynamic user experiences that adapt seamlessly. Although box-sizing: border-box has long been a staple for managing box dimensions, the incorporation of stretch provides another layer of flexibility. As we continue to embrace and implement new CSS features, we not only enhance our layouts but also simplify our maintenance processes, paving the way for a more intuitive approach to web design.
The Future of CSS with Stretch
Looking forward, the introduction of the stretch keyword sets a promising precedent for future developments in CSS. As browsers continue to evolve, it is essential for developers to stay informed about new features and how they can improve workflow efficiency. The versatility of stretch, particularly in relation to padding and the box model, demonstrates its potential to become an essential tool in the developer’s toolkit. By utilizing this new property, we can create more responsive designs that offer a uniform look across various devices and screen sizes.
As we adapt to these new features, it is crucial to maintain a balance between innovation and stability. While embracing stretch, developers should also continue to consider browser compatibility and user experience. Creating fallback methods using the @supports rule is a wise practice, ensuring that our designs remain accessible across different platforms. Ultimately, the stretch keyword, despite being a minor addition to the CSS specification, exemplifies how even small improvements can lead to significant advancements in web development methodologies.